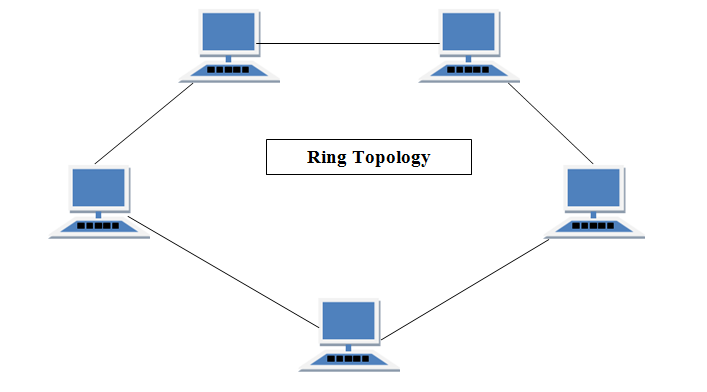
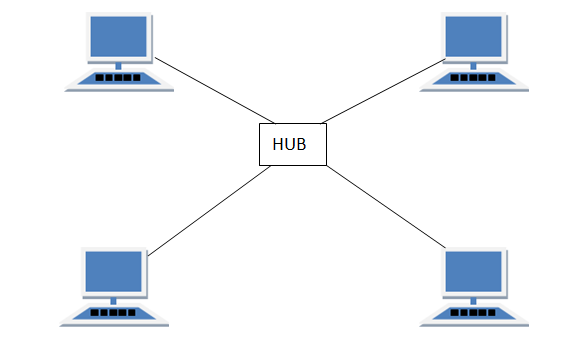
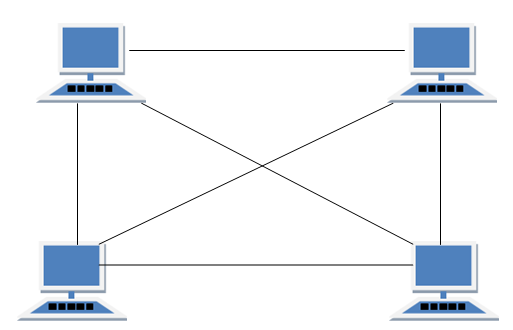
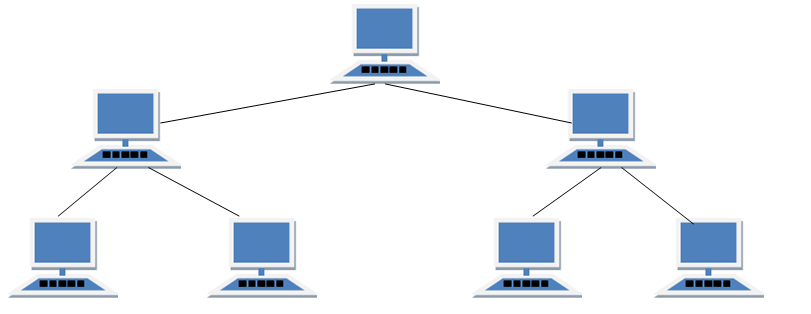
·
Network is a
collection of two or more computers as well as other related devices.
Advantages and
Disadvantages
ADVANTAGES:
Ø Reduce costs
§ Everyone in
your home or office can share a single printer and a single high speed internet
connection at the same time.
Ø Increased
Efficiency
§ You can
access data, pictures, and many other files on any connected computer without
having to save them into a flash drive or USB flash drive or burning them in a
CD.
Ø Economical
§ Purchasing
software network license is relatively cheaper than purchasing individual
license.
Ø More
productivity
§ Shared
internet access means no one needs to wait to use the Internet or email.
Everyone can work simultaneously.
Ø Increase
access to communication channels
§ You can
communicate with others in the network using the email or an Instant Messaging
(IM) software.
Ø More
efficient patching of software
§ Software
updates need only to be installed once. A patch is a piece of software design
to fix or update the data of the computer program.
DISADVANTAGES:
Ø Network
Failures
§ If the
network fails, the users lose access to information and the ability to
communicate electronically
Ø Server Error
§ In a
server/client relationship network, server faults may prevent you from using
some applications, or even accessing your computer
Ø Prone to
hackers
§ Your system
is open to hackers, especially if it is connected to the Internet at all times.
Ø Prone to
virus
§ Networks are
vulnerable to virus attacks. A virus is introduced in one workstation can
spread quickly to other workstations.
Ø Distance
Problem
§ Resources,
such as printers, might be located too far from your table.
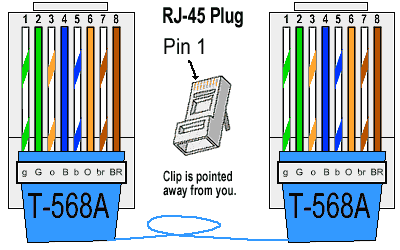
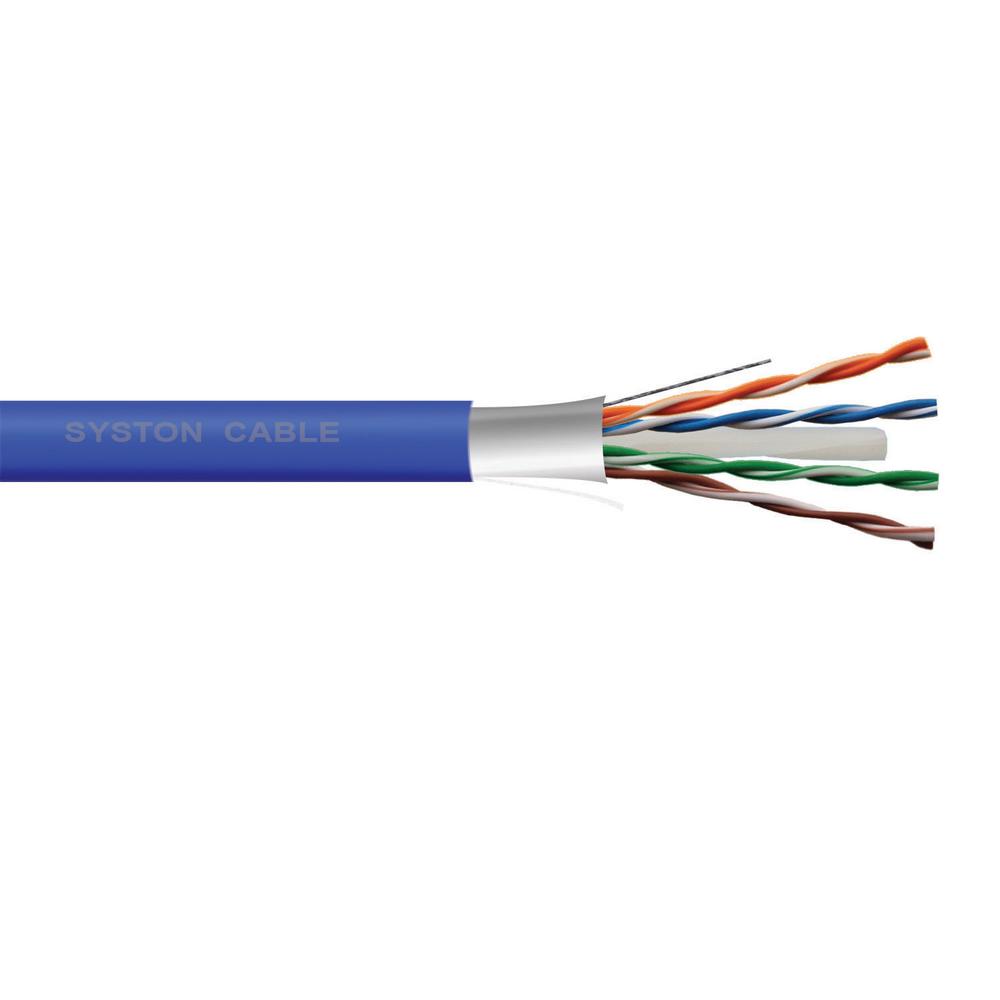
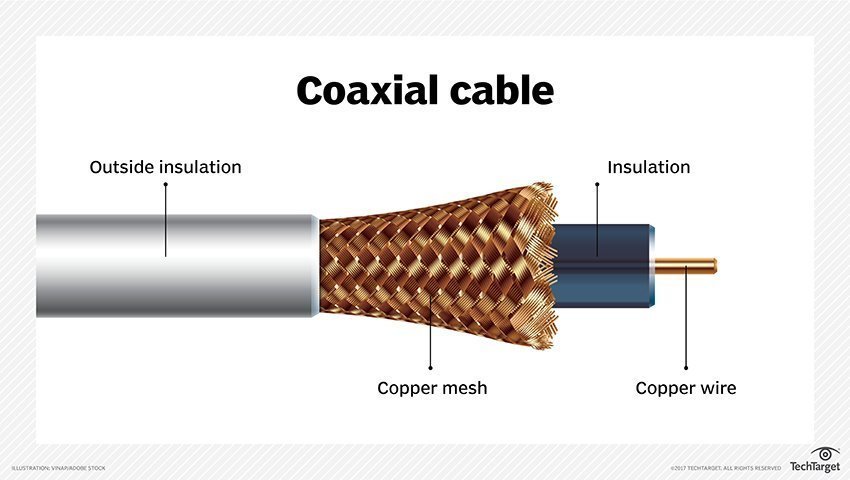
Network Media
Types:
Ø Wired
Network
· It is the
most efficient and practical method of networking where computers are connected
with cables.
Ø Wireless
Network
· It is a
computer network that is not connected by cables of any kind.
Types of Network
PAN (Personal Area Network)
v A
personal area network, or PAN, is a computer network that enables communication
between computer devices near a person. PANs can be wired, such as USB or
FireWire, or they can be wireless, such as infrared, ZigBee, Bluetooth and
ultra wideband, or UWB.
LAN
(Local Area Network)
v A computer
network that links devices within a building or group of adjacent buildings.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
v Is a network that
interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic area or
region larger than that covered by even a large local area network (LAN)
but smaller than the area covered by a wide area
network (WAN).
WAN (Wide Area Network)
v Is simply a
network consisting of interconnected LAN. It is usually dispersed over a very
wide area, and it is not uncommon to see WANs reaching across continents to
link office networks with one another in serval international branch offices.